Building Construction Process
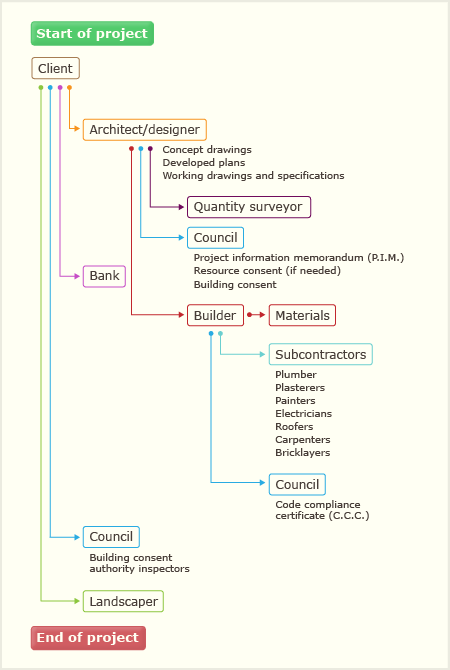
Your building project might be quick and simple or complex. It might be an alteration, a renovation or a completely new build. It could be a seaside holiday house or a multi-unit central city apartment building. The size and complexity of the finished build can affect the duration and complexity of the process. Whatever you're planning, you should generally follow these stages: 1 – Planning a successful build Get your ideas together, separating out what you must achieve and would like to achieve, so that you can think about priorities, budget and timing. You can get some idea of cost from designers or builders, so that you know whether it’s a realistic project. The location of your land, and the position of your building site on it, can have a big impact on your project.
- Commercial Building Construction Process
- Building Construction Products
- Building Construction Process Step By Step Pdf
You need to think about the finished building and how it needs to sit in relation to:. sun. wind. water, electricity and other services. boundaries (a registered surveyor can remove uncertainty).
neighbours (preserve your privacy and theirs). access onto and around the site (for example, paths, driveways and door placement). any hills or slopes (and how they might affect your finished height and width). existing features that you want to retain (for example, trees or outbuildings). If you're planning a rural build, there might be other things to think about.
For example, do you need a septic tank? Will you have to store your own emergency water supply for putting out fires?
You might be surprised to know that some renovation projects can be more complicated than a new build. Talk to your council to get a better understanding of your land, how your ideas will fit and whether you'll need a building consent, resource consent or any other permits. The council can also produce a project information memorandum (PIM), a report specific to your project that can make planning and design easier and more accurate.
As your ideas come together, think again about what you can afford and how you will pay for it. When you're choosing people to do the work, you need to think about:. how involved you will be (realistically, this depends on your skills, energy and other commitments. There are advantages and disadvantages in doing the work yourself.
It might seem cheaper but you need to know what you are doing and your work must still comply with the Building Code.). who you have in mind (architect, builder or a combination) and:. whether they're available. whether they usually work with another building professional. if you're putting them together, will they work well together?. any legal restrictions on who can do the work (for example, if there is restricted building work). who will project manage the work.
Has more details. Includes some things you might need to consider. Highlights some of the differences.
Outlines why you might need specialists. You don’t have to decide everything at this stage, but the more you find out early on, the better informed you and your plans will be. Get your design right Brief your designer well, telling them what you want and how much you have to spend. Agree on concept drawings.
Once you have the full design, go through it in great detail. Try to consider it from every angle, time of day and stage of life including:. how you will use the space. what it will look like. whether there will be enough light inside. what building materials you'll use.
Your plans form the basis of your building consent application, if you need one. You can change them after building consent has been issued, by talking to your council, but there will be time delays and could be additional costs. This applied to every part of the plan, including the materials specified. Any variation from the consented plans could also affect progress, increase cost and delay final sign-off.
Get the right people for your project If you’re going to manage the project, be aware of your responsibilities. If you’re not the project manager, you still have overall responsibility for making sure everything in the building consent happens. Confirm who the project manager is in your design and building contracts (it could be your architect, designer, builder or a professional project manager). It’s often part of the project manager’s role to arrange the builder and tradespeople. Work out if that’s how you will do it, and include this in any contract. You can also hire a quantity surveyor to confirm how much of each material is needed, and provide a cost estimate based on your plans. Approach a shortlist of builders and ask for detailed quotes (not estimates), based on the project plans and/or the quantity surveyor’s report.
Make sure they can work within your timeframe. When comparing quotes, ensure they include the same scope of building work, materials, fixtures and finish so that you can accurately compare them. Follow the same process to engage subcontractors if you are hiring them. Subcontractors often contract directly to the main contractor. Contracts Formalise all roles in legal contracts, spelling out what you mean so that all parties have a clear understanding.
Get a written contract with your builder, including details of guarantees, payment schedules and completion dates. They will probably provide a contract, but you can ask for changes or even provide your own. Whichever you choose, make sure it covers everyone's needs and involve your lawyer. Make sure you have the funds to pay for the project before the work begins and understand the payment terms agreed with the building contractor.
As the project progresses, think carefully before agreeing to pay more than the agreed cost of any work that has been completed or the agreed cost of any materials that have been supplied when you make any payments. Insurance Find out how to protect yourself during the project by talking to your insurer and possibly your bank.
Your insurer may want information about your contractors' insurance and indemnities during a build. If you have a mortgage on your property, your bank may require you to keep them informed of significant changes to your property. If you are using a designer or architect, they should have professional indemnity insurance, to ensure they can pay for repairs if any problems occur as a result of their design. Plan for health and safety Have a health and safety plan in place from day one of construction, and make sure everyone keeps to it.
Understand your obligations under the Health and Safety at Work Act. Should be a priority. 2 – Get a building consent Review your plans and budget You’re about to apply for building consent, so review your plans and budget. This is the time to decide whether you need to make any changes. If you want to make variations later, you will need to apply to amend the consent, pay a fee and potentially delay your project. Apply for a building consent and any other consents or permits Make sure the person completing the application knows what to do and how to make a good application.
It has to include all of the requested information, including detailed drawings and evidence of compliance with the Building Code. If you have restricted building work, you need to name your licensed building practitioner in the building consent application or as soon as you appoint someone. If you require resource consent or any other permits, apply for them as well. If you haven't already got a PIM, you can order one at the same time as you apply for building consent (although it will probably help your planning if you get it earlier).

Think about your timing. Your building consent will lapse if you don’t start the building work within 12 months, unless you have arranged an extension with your council. So give yourself and your building team enough time to complete the project.
3 - Build to the consent Begin construction Once you have building consent, construction can begin. As soon as you know the start date, you need to tell your council. This date is important as you need to start your project within 12 months of receiving your building consent and finish it within two years.
It might seem a long way off, but the date will be used in the council's final project sign-off, and is part of the information you need to gather throughout the project. You or your project manager, builder or architect need to monitor progress and keep the council informed. Organise inspections and ensure they happen. If your work is not progressing as planned, that's another reason to talk to your council. They can help you identify and document variations or amendments to your building consent. Pay bills as milestones are met or as you've agreed in your contracts. Collect energy work certificates for electrical and gas work as it is finished.
Keep them on site with your other papers, as your council will want to see them before they sign-off your code compliance certificate (CCC). 4 – Sign-off and maintain your property Complete your project Ensure everything has been done as set out in your building consent, plans and contracts. You need to let your builder know of any problems within 12 months of the end of the build. You also need to make all final payments, as agreed in your contracts.
Ensure all council fees have been paid as well, so that you can get council sign-off in the form of a code compliance certificate (CCC). If more inspections were required or they took longer than originally anticipated, there may be additional fees. These may not be calculated until after your final inspection, but will need to be paid before your code compliance certificate is issued. Apply to your council for your code compliance certificate (CCC). The council may need a few days’ notice to review your project before they make their final inspection. Maintenance protects your investment Your contractors need to let you know about any required maintenance related to products or materials. You'll need to keep to the instructions so that any warranties and guarantees are effective.
For most domestic building projects, the code compliance certificate (CCC) is the end of the inspection process. However, if your house has a specified system, such as a cable car, it will need regular, ongoing monitoring for safety reasons. This information is published by the Ministry of Business, Innovation and Employment’s Chief Executive.
It is a general guide only and, if used, does not relieve any person of the obligation to consider any matter to which the information relates according to the circumstances of the particular case. Expert advice may be required in specific circumstances. Where this information relates to assisting people:. with compliance with the Building Act, it is published under section 175 of the Building Act. with a Weathertight Services claim, it is published under section 12 of the Weathertight Homes Resolution Services Act 2006.
Commercial Building Construction Process
Construction of residential building required following paper work before the start of actual construction. These steps are;. Preparation of drawings as per requirements of consumers.
Estimation of material cost, labor cost & contingencies. Approval of drawings & estimates from Client. Approval of drawings from City Development Authority.
It is most important because residential building drawings should meet the authority defined rules. Start of construction work either through contractor or labor hired on daily basis.
Marking of plot boundaries. Cleaning of plot. Preparation of site layout as per drawing. After the completion of documentation work, the actual construction on plot begins.
Following are the steps; Earth Work Generally excavation is carried out for the construction of wall foundations. Excavation should be carried out as per the drawings defined lengths & widths. After excavation, layout the foundation and backfill the remaining excavated area around foundation with soil. Floor levels of residential buildings are higher than the natural ground level. Fill the area with soil up to floor levels and compact the soil. Now earth work of residential building is finished.
Concrete Work in Foundation It is very necessary to check the levels of foundation before concrete work. There are patches where excavated depth slightly exceeds and vice versa. Level the foundation base to same level.
Building Construction Products
Now pour the concrete as per drawing specs. Generally concrete of ratio 1:4:8 is used for foundation. Sometimes it is even 1:5:10 or 1:6:20. Here 1:4:8 means; 1 part cement per cubic 4 parts of sand per cubic 8 parts of coarse aggregates Depth of foundation varies from 9” to 18” and normally for most of the cases it is considered as 12’’ depth.
Keep foundation width equals to its depth. Damp Proof Coarse (D.P.C) To protect walls from moisture, a layer of damp proof coarse material is laid down at floor level. Thickness of this concrete layer is 0f 1 inch. Material of damp proof coarse layer consists of concrete ratio 1:1.5:3 with a mixture of water proof material 1kg/bag.
Masonry Work Masonry work is carried out with cement mortar. Cement mortar is a mixture of cement & sand. Ratio of cement mortar varies from 1:4 to 1:6. Here (1:6) mean, 1 part cement and 6 parts of sand. Dampen about 25 bricks with a hose pipe and clean away all loose dirt from the top of footing and moisten about a meter of surface at one end of the foundation with the hose pipe.

Building Construction Process Step By Step Pdf
Throw a mortar line just behind the threaded level line and lay bricks on the mortar bed. Make sure bricks exactly follow the threaded horizontal level line. Lintel Masonry work of buildings is carried out in one go till roof. Openings for windows & doors are left during masonry works. Reinforced cement concrete beams are laid down on the top of openings. So, those loads of structure above openings not directly come on to the door frames.
Roofing Roof slab of building is poured after completion of masonry works. Now a days, roofing is of reinforced cement concrete slab. Slab thickness & reinforcement details should be according to approved drawings.
Plastering & Pointing Form work is removed after 14 days of slab pouring. Now plaster work begins. Mortar for plaster work is generally of 1:3 or 1:4 is used. Thickness of plaster layer should not be more than 0.75inch.
Cure the surface about 7 days. So that, plaster gain proper strength. Generally, internal walls of buildings are covered with plastered layer and external walls with pointing. It is better plaster the external walls rather than pointing.
Doors & Windows Traditionally, doors and windows of woods are used. But, steel & aluminum is also not a bad choice. In case of wooden doors & windows, frames are fixed in walls during masonry work. Panels are then fixed with hinges after plaster work. Steel and aluminum doors are fixed after completion of paint work.
Services Services are very important for every single house. Different types of services are provided during construction. These are Electricity supply, gas supply, water supply, sanitary etc. Conduits for electric supply are fixed in walls before plastering. Similarly water supply and sanitary lines are also laid before pouring of building floor. Note that gas lines are not fixed in walls or slabs.
Gas line remains open in air.